Ranking-Aware Contrastive Learning with Large Language Models
Completed in Retrieval Augmented Generation, 2023
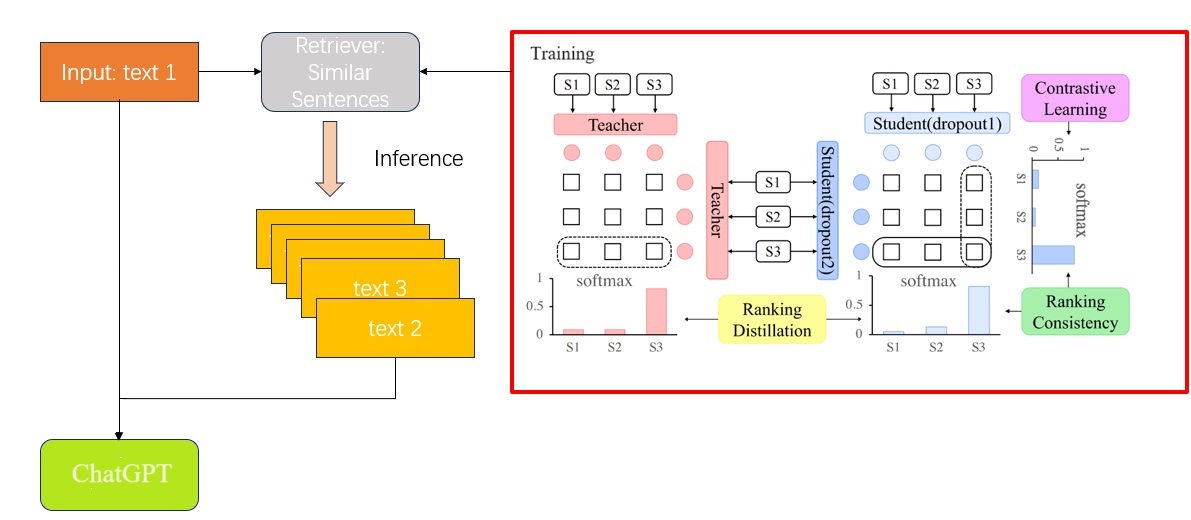
Generating high-quality word and sentence representations is a foundational task in natural language processing (NLP). In recent years, various embedding methodologies have been proposed, notably those leveraging the capabilities of large language models for in-context learning. Research has shown that language model performance can be enhanced by integrating a query with multiple examples. Inspired by this research, this project explores the use of a contrastive learning framework combined with ranking knowledge to enhance the generation and retrieval of sentence embeddings, aiming to more accurately identify the most similar sentences in in-context learning scenarios.
The initial experiment assessed various contrastive learning frameworks, revealing that the DiffCSE framework slightly outperforms the SimCSE framework. Substituting the pre-trained BERT model with the large language model “OPT-2.3b” can further enhance contrastive learning outcomes. Subsequently, the RankCSE model, which integrates ranking consistency into the framework, yielded additional performance gains. Moreover, the application of ranking distillation, leveraging insights from multiple pre-trained teacher models, demonstrated that an optimal ratio of distilled knowledge (2:1) from DiffCSE and SimCSE maximizes the RankCSE model's efficacy. Finally, evaluations across different supervisory approaches and ranking algorithms indicated that unsupervised learning combined with ListMLE for parameter updates results in superior performance.
Future research could involve deploying the pre-trained RankCSE model as a retriever in conjunction with large language models such as ChatGPT to assess its efficacy in real-life scenarios.